Every journey begins with one step in the right direction. In order to know the direction to take, it is important to know where you are at right now.
Definition
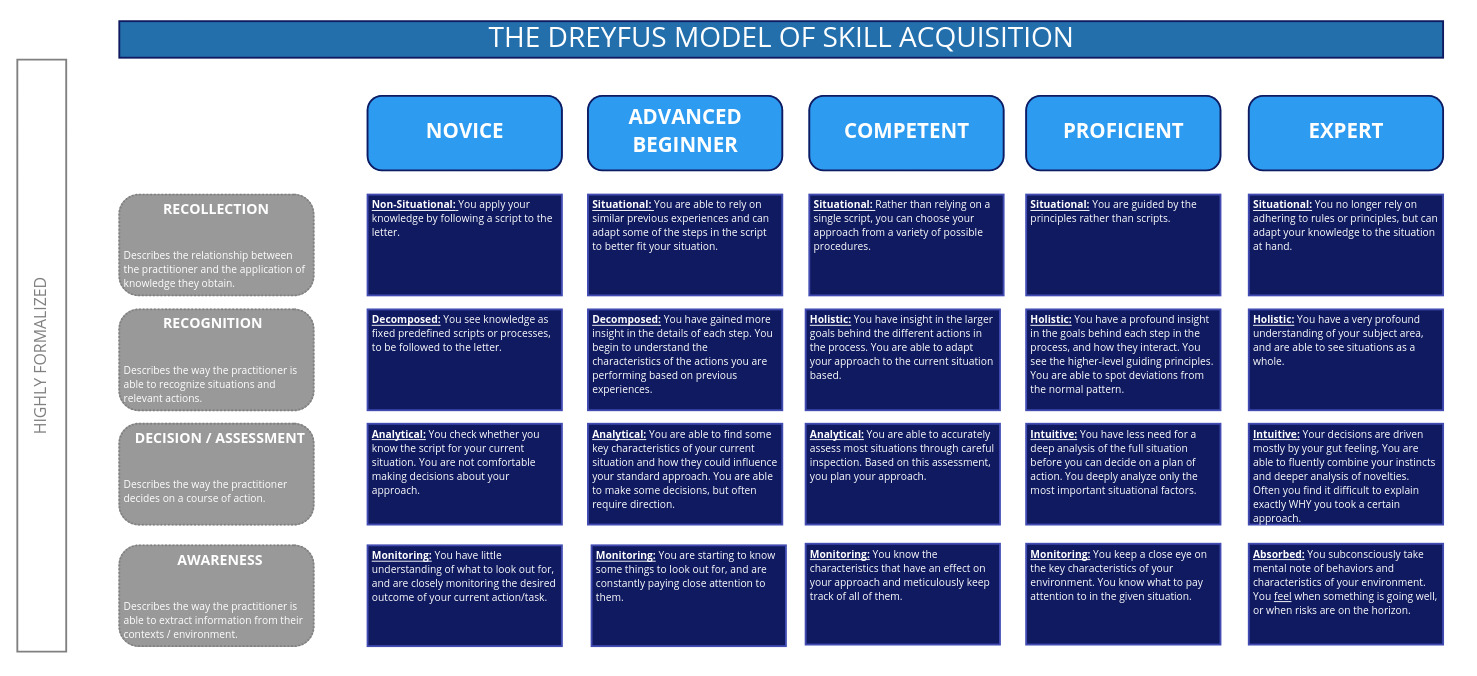
The Dreyfus model of skill acquisition is a formal framework that defines five distinct stages of mastery, showing how learners progress and change in their application of skills and knowledge. These stages are Novice, Advanced Beginner, Competent, Proficient, and Expert.
Key Components
The different skill level are described across these four main areas:
- Recollection: The relationship between the practitioner and their application of knowledge.
- Recognition: The practitioner’s ability to recognize situations and relevant actions.
- Decision: The practitioner’s process of deciding on a course of action.
- Awareness: The practitioner’s ability to extract information from their context or environment.
Breakdown of skill levels
Novice
- Recollection: Non-Situational. The learner applies their knowledge by following a script to the letter.
- Recognition: Decomposed. The learner sees knowledge as fixed predefined scripts or processes, to be followed to the letter.
- Decision: Analytical. The learner checks whether they know the script for the current situation. They are not comfortable making decisions about their approach.
- Awareness: Monitoring. The learner has little understanding of what to look out for, and is closely monitoring the desired outcome of their current action/task.
Advanced beginner
- Recollection: Situational. The learner is able to rely on similar previous experiences and can adapt some of the steps in the script to better fit their situation.
- Recognition: Decomposed. The learner has gained more insight in the details of each step. They begin to understand the characteristics of the actions they are performing based on previous experiences.
- Decision: Analytical. The learner checks whether they know the script for the current situation. They are not comfortable making decisions about their approach.
- Awareness: Monitoring. The learner knows some things to look out for, and is constantly paying close attention to them.
Competent
- Recollection: Situational. Rather than relying on a single script, the learner can choose their approach from a variety of possible procedures.
- Recognition: Holistic. The learner has insight in the larger goals behind the different actions in the process. They are able to adapt their approach to the current situation.
- Decision: Analytical. The learner is able to accurately assess most situations through careful inspection. Based on this assessment, they plan their approach.
- Awareness: Monitoring. The learner keeps a close eye on the key characteristics of their environment. They know what to pay attention to in the given situation.
Proficient
- Recollection: Situational. The learner is guided by the principles rather than scripts.
- Recognition: Holistic. The learner has a profound insight in the goals behind each step in the process, and how they interact. They see the higher-level guiding principles. They are able to spot deviations from the normal pattern.
- Decision: Intuitive. The learner has less need for a deep analysis of the full situation before they can decide on a plan of action. They deeply analyse only the most important situational factors.
- Awareness: Monitoring. The learner knows the characteristics that have an effect on their approach and meticulously keeps track of all of them.
Expert
- Recollection: Situational. The learner no longer relies on adhering to rules or principles, but can adapt their knowledge to the situation at hand.
- Recognition: Holistic. The learner has a very profound understanding of the subject area, and are able to see situations as a whole.
- Decision: Intuitive. The learner’s decisions are driven mostly by their gut feeling. They are able to fluently combine their instincts and a deeper analysis of novelties. Often they find it difficult to explain exactly WHY they took a certain decision.
- Awareness: Absorbed. The learner subconsciously takes mental note of behaviours and characteristics of their environment. They feel when something is going well, or when risks are on the horizon.
Background
Origin
The Dreyfus model was developed by Stuart E. Dreyfus and Hubert L. Dreyfus at the University of California, Berkeley. It was first introduced in their 1980 paper, “A Five-Stage Model of the Mental Activities Involved in Directed Skill Acquisition.”
Application
Comparisons
The Dreyfus model can be compared to other skill acquisition frameworks, such as the Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning Domains, which categorizes educational goals and objectives. While Bloom’s Taxonomy focuses on cognitive skills, the Dreyfus model emphasizes practical skill development and the transformation in thought processes.
Examples
Tailoring coaching approach to the learner’s skill level
In general, the more experienced one becomes, the more they start internalizing a concept of “the bigger picture”. Inexperienced practitioners of a skill are pleased when someone provides them with clear-cut instructions, especially if they’ve heard applying these instructions will lead to certain success. Adapt your coaching and teachings styles to the needs of the learner.
Further Exploration
- Dreyfus, Stuart E; Dreyfus, Hubert L. (1980). A Five-Stage Model of the Mental Activities Involved in Directed Skill Acquisition. 'Berkeley': University of California.
http://www.dtic.mil/cgi-bin/GetTRDoc?AD=ADA084551&Location=U2&doc=GetTRDoc.pdf. - Hunt, A. (2008). Pragmatic Thinking and Learning: Refactor Your wetware. The Pragmatic Bookshelf. isbn: 9781934356050.
https://pragprog.com/titles/ahptl/pragmatic-thinking-and-learning/. - Hoover, D.; Oshineye, A. (2009). Apprenticeship Patterns. O'Reilly Media, Inc.. isbn: 9780596518387.
https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/apprenticeship-patterns/9780596806842.